- Radio Waves
- what exposure to radio waves?
what exposure to radio waves?
As with light, when a radio wave strikes an object, part of the energy it carries is reflected, part is transmitted and yet another part is absorbed.
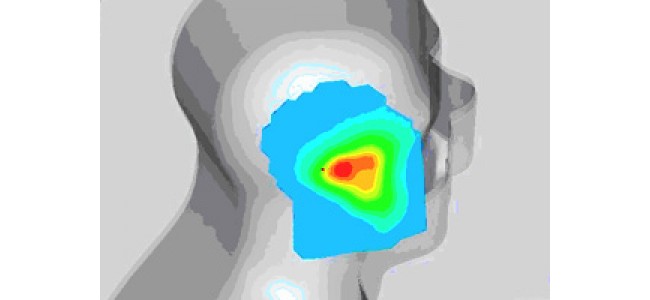
This phenomenon also applies to the body of a mobile user, as with any other device generating waves: this is what is called the « specific absorption rate » (SAR).
This benchmark serves to measure maximum exposure to radio waves: the SAR is the amount of energy absorbed relative to mass. Its measurement is expressed in watts per kilogram (W/kg).
Variable exposure depending on conditionsThe SAR of a mobile is the maximum level of radio waves to which a user may be exposed during communication. It is now part of specifications describing devices.All mobile phones purchased through conventional distribution channels have SAR lower than 2 W/kg – the limit-value for local exposure of the head or trunk to radio waves. Device manufacturers are required to display the SAR in their instructions.In practice, during communication, the actual exposure of the mobile user is always lower than SAR indicated because mobile phones rarely operate at maximum power. This actual exposure of the body varies primarily according to the transmission power: the higher it is, the greater the exposure of the user. It increases, especially when the user phones in poor conditions: at the edge of a coverage area (for example far away from base station), underground, during high-speed travel by train or car, etc.
for more information :
- ICNIRP website
- power and exposure to radio waves from mobile devices on the GSMA website (under « Mobile Devices »)
- our best practise section
Other parameters may affect actual exposure, such as the positioning of the mobile telephone (away from or close to the body), the use, or not, of an earpiece, etc.
New uses of the mobile phone
In addition, new uses of the mobile phone (Internet, photos, videos, TV, music, email, etc.) have naturally tended to reduce the exposure of the head and trunk of users away from the terminal, unlike conventional calls where the apparatus is positioned near the ear. The use of a headset is also recommended for telephone calls if users wish to reduce radio exposure as it increases the distance between handset and head.